Pattern Matching on 2D Lidar Data
Sometimes we need to interact with a specific object in a specific way. To do this, we need to find it first!
In this post, i will introduce a simple but effective Pattern Matching technique. This technique uses 2D Lidar Data and tries to find a pattern inside of it. You can use it to find chargers, docking stations, pallets etc.
To process lidar data, i used Point Cloud Library (PCL). PCL is a flexible, strong and time tested point cloud processing library. It already has required capabilities for Pattern Matching. Therefore, we don’t have to re-invent wheel.
The algoritm is as follows:
- Extract clusters. Divide main point cloud into smaller ones. After this step, you will have small point clouds that clustered based on distance. You can see end result below. Each cluster was given a different color.
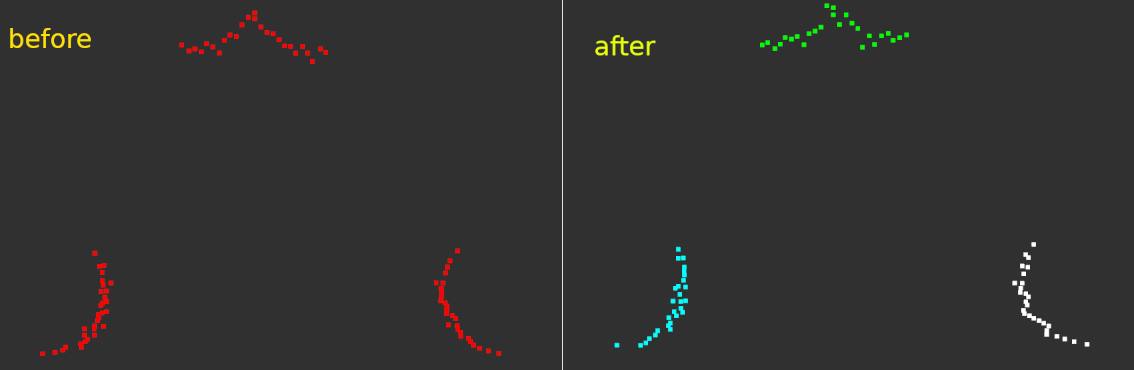
- Run ICP on every cluster. Try to mach every cluster with pattern using Iterative Closest Point (ICP). Since ICP is very sensitive to initial alignment, use difference between cluster and pattern centroids as initial alignment.

- Get best match as result. ICP gives a fitness score to asses match quality. Get best fitness score to determine which cluster is likely the pattern.

Pattern Matcher ROS Package
I have created a ROS Package to demonstrate above algorithm. You can download it from here. To open simulation environment and matcher node, run these commands as in the video below.
export TURTLEBOT3_MODEL=waffle
roslaunch pattern_matcher gazebo.launch
roslaunch pattern_matcher matcher.launch
Notes:
- Currently, all clusters are being used for ICP match. In crowded environments, this will result higher loop times.
- Match quality is inversely proportional to lidar noise. Lower lidar noise gives better match results.
- No matter what lidar you use, there will always be some noise. Therefore match result will be always noisy. If you want to use this technique for something like visual servoing, you should consider using some filter.
Creating Your Own Pattern
This package reads pattern from a pcd file. Default pcd file is located at pattern_matcher/pcd/pattern.pcd. pcd filepath is given to matcher node as pattern_filepath parameter. You can change this parameter to use your own pattern. If you don’t have a pcd file, you can use recorder node to create one.
recorder node collects lidar scans, calculates a mean scan to reduce lidar noise and saves it as pcd file. You can use it by running below command. Parameter desctiptions are located in the launch file.
roslaunch pattern_matcher recorder.launch
matcher node calculates the transformation between lidar’s current position and recording position. Therefore before recording a pcd file, make sure lidar is in ‘desired’ position.